Correction Examen Régional 3APIC Mathématiques 2024 Casablanca Settat
Correction Examen Régional 3APIC Mathématiques 2024 Casablanca Settat
Vous retrouvez sur cette page la Correction Examen Régional 3APIC Mathématiques 2024 Casablanca Settat, disponible en PDF et en vidéo. Préparez-vous bien et nous vous souhaitons la réussite !
Sujet de l’examen
Le sujet en image :
La correction
Exercice 1
- 3x + 2 = x - 1\\
3x - x = -1 - 2 \\
2x = -3 \Rightarrow x = -\frac{3}{2}\\
Donc -\frac{3}{2} est solution de l’équation. - 4x + 2 \leq 7x - 1\\
4x - 7x \leq -1 - 2 \\
-3x \leq -3 \Rightarrow x \geq 1 \\
Tous les nombres supérieurs ou égaux à 1 sont solutions de l’inéquation. - a) On a : (2x - 1)(x + 1) = 2x^2 + 2x - x - 1 = 2x^2 + x - 1\\
Donc 2x^2 + x - 1 = (2x - 1)(x + 1)\\
b) On a : 2x^2 + x = 1 \Rightarrow 2x^2 + x - 1 = 0 \quad \text{(1)}\\
Or d’après la question précédente, on a :
2x^2 + x - 1 = (2x - 1)(x + 1)\\
donc (1) équivaut à :
2x^2 + x = 1 \Rightarrow (2x - 1)(x + 1) = 0 \\
Donc on a :
2x - 1 = 0 \Rightarrow 2x = 1 \Rightarrow x = \frac{1}{2} \\
ou
x + 1 = 0 \Rightarrow x = -1 \\
2x^2 + x = 1 a pour solutions \boxed{x = \frac{1}{2}} et \boxed{x = -1}\\
Exercice 2
- \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;3x + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; x + 4y = 17 \end{array}\right.\\
par substitution :
\Rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;3x + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; x = 17 - 4y \end{array}\right.\\
\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;3(17-4y) + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; x = 17 - 4y \end{array}\right.\\
\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;51 - 12y + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; x = 17 - 4y \end{array}\right.\\
\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;-12y + 2y = 14 - 51 \\ \;\;\; x = 17 - 4y \end{array}\right.\\
\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;-10y = -37 \\ \;\;\; x = 17 - 4y \end{array}\right.\\
\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;y = \dfrac{37}{10} \\ \;\;\; x = 17 - 4 \times \dfrac{37}{10} \end{array}\right.\\
\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;y = \dfrac{37}{10} \\ \;\;\; x = \dfrac{11}{5} \end{array}\right.\\
Le couple (\dfrac{11}{5};\dfrac{37}{10}) est solution du système. - Choix des inconnues :
Soit x le prix d’un morceau de pain et y le prix d’un morceau de gâteau.
Mise en système :
Hamid achète 3 morceaux de pain et 2 morceaux de gâteau, donc :
3x + 2y = 14\\
Amina achète 2 morceaux de pain et 8 morceaux de gâteau pour 34 dhs, donc :
2x + 8y = 34\\
Soit : \left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;3x + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; 2x + 8y = 34 \end{array}\right.\\
Résolution :
\left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;3x + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; 2x + 8y = 34 \end{array}\right.\\
En divisant la deuxième équation par 2, on a :
\left\{\begin{array}{l}\;\;\;3x + 2y = 14 \\ \;\;\; x + 4y = 17 \end{array}\right.\\
D’après la question précédente, le couple (\dfrac{11}{5};\dfrac{37}{10})est solution du système.
Ou le couple \boxed{(2{,}2 \ ; \ 3{,}7)} est solution du système.
Conclusion :
– Le prix d’un morceau de pain est 2,2 dhs.
– Le prix d’un morceau de chocolat est 3,7 dhs.
Exercice 3
- a)
b) Graphiquement l’image de 1 est 2.
c) Le nombre qui a pour image -2 par la fonction g est -1
g) g est une fonction linéaire donc : g(x) = ax\\
Or a = \dfrac{g(x)}{x} = \dfrac{g(2)}{2} = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2\\
Donc g(x) = 2x\\ - f est une fonction affine : f(x) = -2x + 4\\
a) L’image de 3 : f(3) = -2 \times 3 + 4 = -6 + 4 = -2\\
Donc l’image de 3 par f est -2
b) On doit résoudre f(x) = -2 \Leftrightarrow -2x + 4 = -2 \Leftrightarrow -2x = -2 -4 \Leftrightarrow -2x = -6 \Leftrightarrow x= \dfrac{-6}{-2} \Leftrightarrow \boxed{x = 3}
c) \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}\hline x & 3 & 3 & 0 & 2 \\\hline f(x) & -2 & -2 & 4 & 0 \\\hline\end{array}\\
Exercice 4
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \text{Valeur} & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ \hline \text{Effectif} & 5 & 1 & 3 & 2 & 8 & 6 \\ \hline \text{ECC} & 5 & 6 & 9 & 11 & 19 & 25 \\ \hline \end{array}\\
- On a : 5 + 1 + 3 + 2 + 8 + 6 = 25\\
Donc le nombre de joueurs de cette équipe est \fbox{25}\\ - Le plus grand effectif est 8 associé à la valeur 4 donc le mode de cette série statistique est \fbox{4}.\\
- Soit m la moyenne :
m = \dfrac{0 \times 5 + 1 \times 1 + 2 \times 3 + 3 \times 2 + 8 \times 4 + 5 \times 6}{25} = \boxed{3}\\
La moyenne arithmétique de cette série est \fbox{3}.
Exercice 5
- Image de B par la translation t donc \overrightarrow{BE} = \overrightarrow{AC} (1)
- Image de C par la translation t donc \overrightarrow{CF} = \overrightarrow{AB} (2)
- De (1) et (2), on a \overrightarrow{BE} = \overrightarrow{CF} donc BCFE est un parallélogramme par conséquent \overrightarrow{EF} = \overrightarrow{BC}
- Donc l’image de E par la translation qui transforme B en C est le point \fbox{F}.
Exercice 6
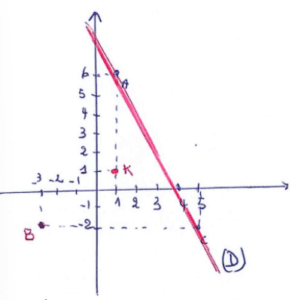
A(1;6), B(-3;-2), C(5;-2), K(1;1), \quad \mathcal{D}: y = -2x + 8- On a \mathcal{D}: y = -2x + 8\\
-2x_A + 8 = -2 \times 1 + 8 = -2 + 8 = 6 \Rightarrow donc y_A = 6 \Rightarrow donc A \in \mathcal{D}\\
-2x_C + 8 = -2 \times 5 + 8 = -10 + 8 = -2 \Rightarrow donc y_C = -2 \Rightarrow donc C \in \mathcal{D}\\
Conclusion: les points A et C appartiennent à la droite \mathcal{D}, donc la droite \mathcal{D} est seulement la droite (AC) - 3.
4. (AB): y = mx + p est l’équation réduite de la droite (AB)\\
Calcul de m :
m = \dfrac{y_B - y_A}{x_B - x_A} = \dfrac{-2 - 6}{-3 - 1} = \dfrac{-8}{-4} = 2\\
Donc (AB): y = 2x + p\\
Calcul de p :
A \in (AB) \Rightarrow y_A = 2x_A + p \Rightarrow 6 = 2 \times 1 + p \Rightarrow 6 = 2 + p \Rightarrow p = 4\\
Conclusion (AB): y = 2x + 4\\
5. KA = \sqrt{(x_A - x_K)^2 + (y_A - y_K)^2} = \sqrt{(1 - 1)^2 + (6 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{0^2 + 5^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5\\
Donc KA = 5\\
6. E est milieu de [AC] soit E(x_E; y_E) donc :
x_E = \dfrac{x_A + x_C}{2} \quad \text{et} \quad y_E = \dfrac{y_A + y_C}{2} \Rightarrow x_E = \dfrac{1+5}{2}, \quad y_E = \dfrac{6-2}{2}\\
\Rightarrow x_E = 3, \quad y_E = 2 \Rightarrow E(3;2)\\
7. (\Delta): y = mx + p \quad (\Delta) \perp (d) \Leftrightarrow m_{\Delta} \times m_D = -1 \\
m_{\Delta} = \dfrac{-1}{-2} \Rightarrow m_{\Delta} = \dfrac{1}{2}\\
Donc : (\Delta): y = \dfrac{1}{2}x + p\\
– Calcul de p
On sait A \in (\Delta) donc y_A = \dfrac{1}{2}x_A + p \Rightarrow 6 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1 + p \Rightarrow p = 6 - \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{11}{2}\\
– Conclusion
\boxed{(\Delta): y = \dfrac{1}{2}x + \dfrac{11}{2}}\\
Exercice 7
- V_1 volume de la pyramide SABC donc :
V_1 = \dfrac{A_{ABC} \times SA}{3} = \dfrac{\dfrac{AB \times AC}{2} \times SA}{3} = \dfrac{\dfrac{4 \times 6}{2} \times 16}{3} = \dfrac{22 \times 16}{3} = 64 \Rightarrow \boxed{V_1 = 64 \text{ cm}^3}\\ - On sait que l’aire EFG = 3 \text{ cm}^2 et l’aire ABC = \dfrac{4 \times 6}{2} = 12 \text{ cm}^2\\
Donc le coefficient de réduction k est défini par :
\dfrac{A_{EFG}}{A_{ABC}} = k^2 \Rightarrow k^2 = \dfrac{3}{12} = \dfrac{1}{4} \Rightarrow \boxed{k = \dfrac{1}{2}}\\
Calcul de V_2\\
V_2 = V_1 \times k^3 = 64 \times \left( \frac{1}{2} \right)^3 = \boxed{8 \text{ cm}^3}\\
Le volume V_2 de la pyramide SEFG est \textbf{8 cm}^3\\
Vous pouvez consulter et télécharger la correction complète en cliquant sur le lien ci-dessous :
Télécharger La correction en PDF
Correction vidéo expliquée – Très bientôt
La correction en vidéo de l’Examen Régional 3APIC Mathématiques 2024 Casablanca Settat sera bientôt disponible. Restez connectés pour une explication détaillée et des conseils pratiques pour mieux comprendre les réponses !
Abonnez-vous à notre chaîne YouTube
Abonnez-vous à notre chaîne YouTube et activez la cloche de notification pour recevoir toutes nos prochaines vidéos, y compris la correction vidéo expliquée de l’examen régional SVT 2024.


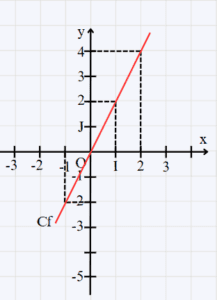 b) Graphiquement l’image de
b) Graphiquement l’image de 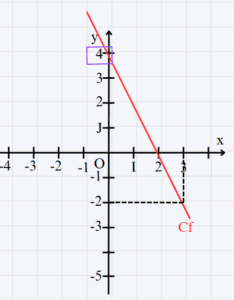
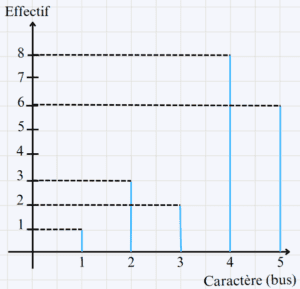
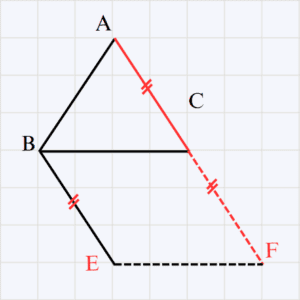
 4.
4.